A Complete Manual for Conducting International Flight Operations
WGS 84 Status
WGS 84 Status
WGS 84 is an Earth-centered, Earth-fixed terrestrial reference system and geodetic datum. WGS 84 is based on a consistent set of constants and model parameters that describe the Earth’s size, shape, and gravity and geomagnetic fields. WGS 84 is the standard U.S. Department of Defense definition of a global reference system for geospatial information and is the reference system for the Global Positioning System. It is compatible with International Terrestrial Reference System.
What flight crews need to know is whether their intended destination is WGS 84 compliant, if it is compliant no additional work is required. If it is not compliant or partially compliant more information is required. Jeppesen publishes a list of WGS-84 compliant countries on the website http://ww1.jeppesen.com/company/publications/wgs-84.jsp.
Jeppesen uses the following terminology on their website:
COMPLIANT (C)
PARTIALLY COMPLIANT (PC)
The country AIP or equivalent publication contains a statement that all latitude/longitude coordinates are referenced to the WGS-84 datum or equivalent.
The country AIP or equivalent publication contains a statement that latitude/longitude coordinates are referenced to the WGS-84 datum or equivalent, but there are exceptions or the detailed AIP information indicates conversion to WGS-84 is not complete.
It is interesting to note that a developed country like Greece is only partially compliant .
The current list of non-compliant aerodromes in partially compliant countries as of this writing are the following:
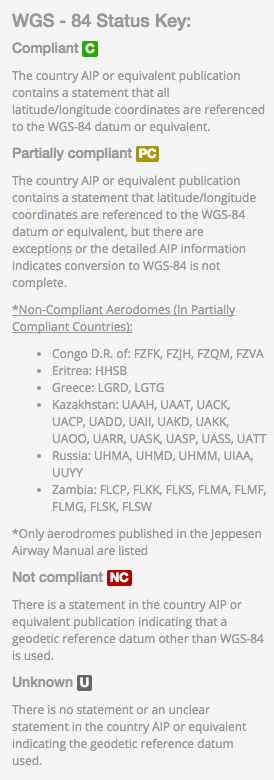
For reference only, visit Jeppesen for current listings.
NON-WGS 84 OPERATIONS PROCEDURES
In countries that are non-compliant pilots must deselect GPS from position sensors and the FMS will revert to a DME/DME position solution. It should also be noted that inconsistencies may occur in GPWS systems, as they are based on WGS 84 data.
The Gulfstream manual says the following regarding operating in WGS 84 countries: “When operating in non-WGS-84 airspace or in countries where the airspace is partially compliant with WGS-84, the FMS with GPS position updating meets the required navigation accuracy and may be used for SIDS, STARS and enroute navigation. When flying ILS, VOR or ADF approaches and missed approach procedures in these two situations, the GPS updating does not need to be inhibited or deselected provided the appropriate raw data is used throughout the approach and missed approach as the primary navigation reference. For countries that are partially WGS-84 compliant, when RNAV (GNSS) approaches are offered, these approaches may be flown using the FMS with GPS position updating provided the approach chart is annotated with “PANS OPS”.
The image at the right represents the differences that would occur in non-WGS 84 compliant countries.
Given the differences in non- WGS 84 countries it is recommended that ACI Pilots review their aircraft specific recommendations for FMS position sensor selection and as of this time opt for ILS or VOR type approaches over GPS, or at a minimum, select GPS approaches that have ground based raw data redundancy.
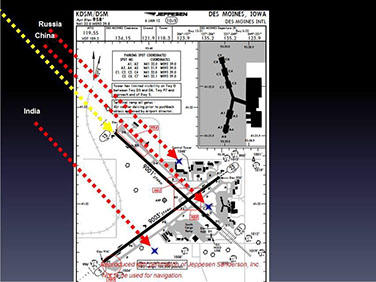
Figure 3 Gribble
JOIN THE CONVERSATION

The material contained on this site is to be used for reference only. You should always follow your primary resources first (aircraft manuals, government regulations, etc.).
Savant Aero is no way affiliated with any aircraft manufacturers.

